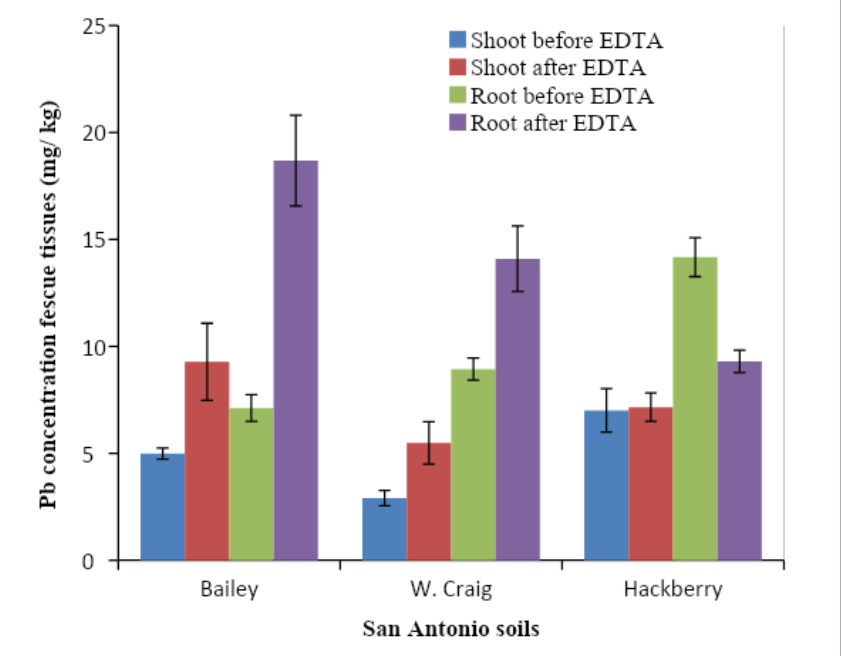
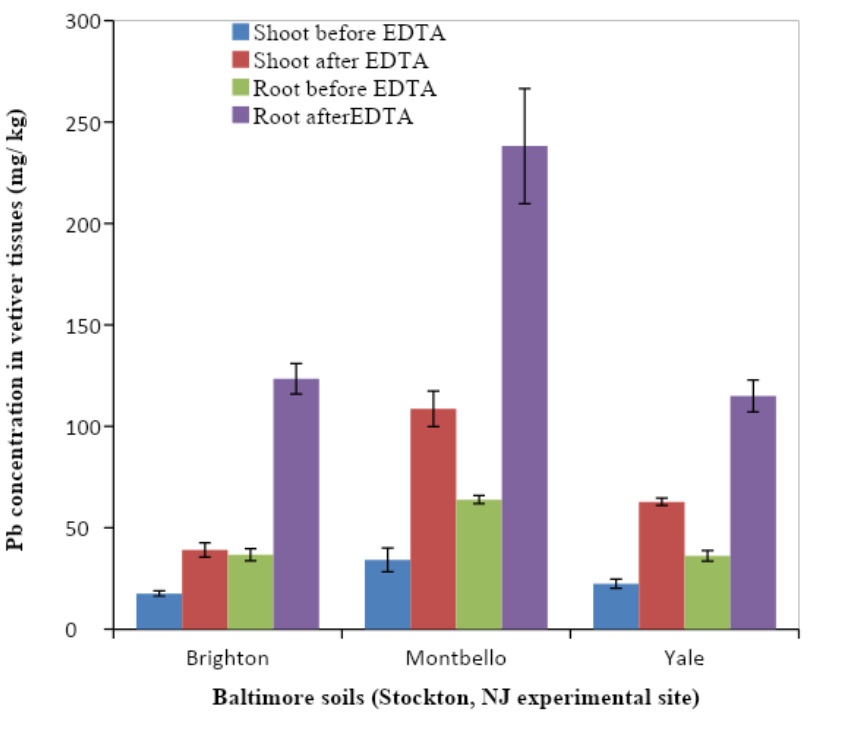
EDTA was applied at a 15 mmol/kg rate to the San Antonio and Stockton sites. Soil, plant, and leaching samples were collected before and 20 days after EDTA treatment. Overall, vetiver grass showed no signs of toxicity to EDTA or any of the lead concentrations. Vetiver and fescue samples were collected before and after EDTA application. As in the previous studies, EDTA increased the lead uptake and translocation in the vetiver samples, with no significant change in fescue (Datta, Sarkar, and Andra).

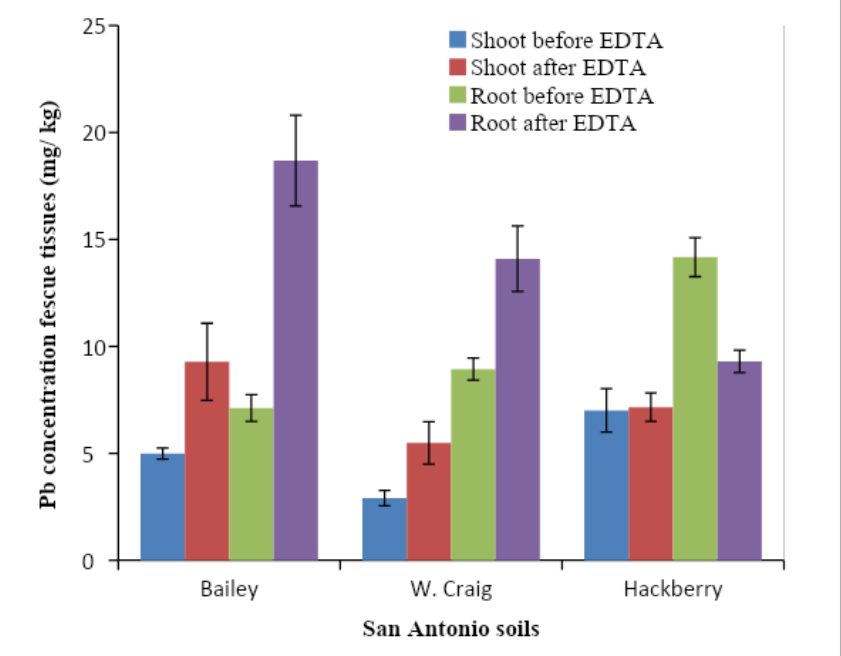
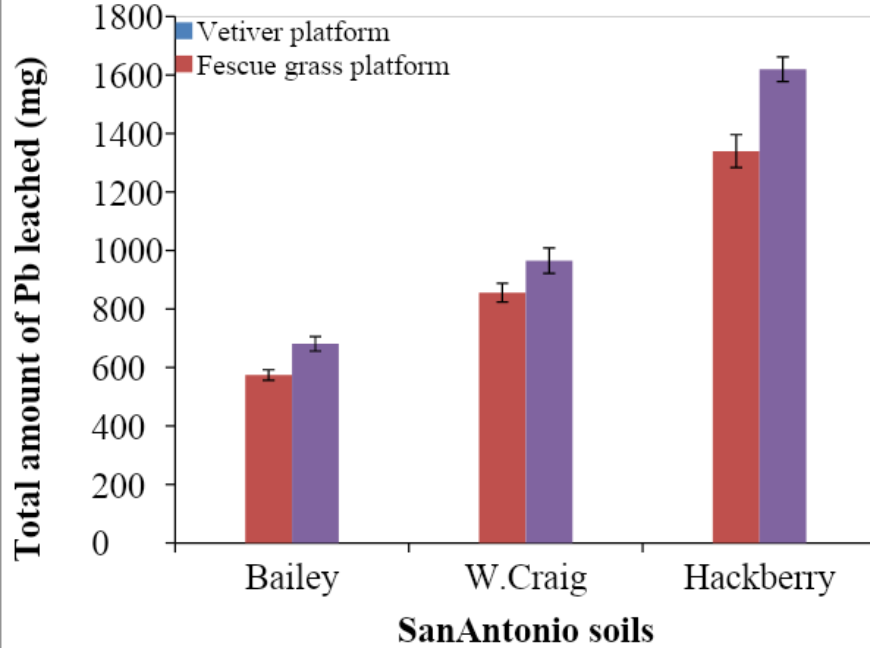
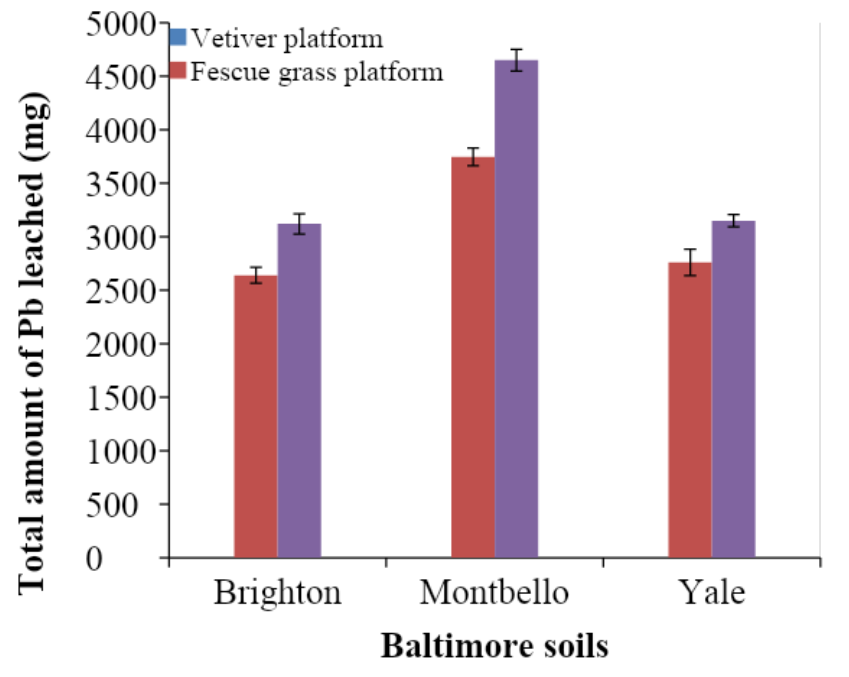
The leached samples showed that lead solubility increased with EDTA application, with fescue leaching more lead than vetiver. Total lead concentrations in the soil were collected and analyzed. The overall results showed that vetiver grass had a lower lead concentration compared to fescue. The EDTA application resulted in enhanced uptake of lead by vetiver and increased solubility of lead (Datta, Sarkar, and Andra).